The UN – a meeting point for peace
The United Nations (UN) was established in 1945, shortly after World War II. The hope was that an international organisation could be a tool to prevent future wars and work for lasting peace. Fifty-one countries entered into an agreement called the UN Charter. The UN Charter officially entered into force on October 24, 1945, which is why UN Day is on the 24th of October. Today, the vast majority of countries in the world are members of the UN.
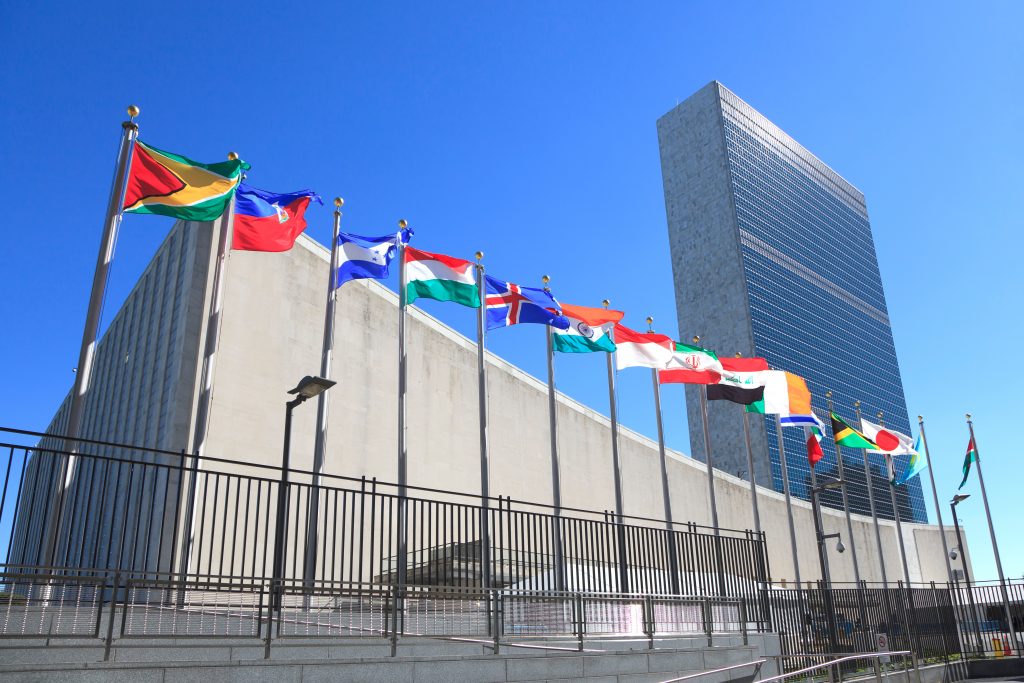


The UN logo shows a map of the world and olive branches. The UN’s headquarters are located in New York in the US.
The Secretary-General
The UN is headed by a Secretary-General. The Secretary-General is appointed by the General Assembly every five years. The Secretary-General has ultimate responsibility for leading the day-to-day work of the UN. Another important task is to work politically to prevent conflicts from starting, developing or spreading. The Secretary-General is also responsible to raising problems that could threaten world peace with the Security Council.
The UN’s work
The UN is a big organisation that consists of a number of departments that are responsible for different areas that the UN works in. The UN’s work can be divided into the three core areas: peace and security, human rights, and sustainable development.
Peace and security
The UN Security Council has primary responsibility for peace and security. The Security Council’s primary responsibility is to maintain peace and security in the world. If peace is threatened, the Security Council will usually urge the parties to find a peaceful solution, including by initiating mediation. The Security Council can also enforce decisions by, among other things, ordering economic sanctions or initiating military action. An example of military action is the UN peacekeeping forces. The forces consist of military personnel on loan from various member states.
The Security Council consists of representatives from 15 member states. Five of the countries are permanent members, the others are elected for two-year terms. The United States, Great Britain, France, Russia and China are permanent members. In the UN, only the Security Council can use military force, and all member states are obliged to follow the decisions of the Security Council.
Human rights
Another of the UN’s core areas is work to ensure the fundamental rights of all people. As early as 1948, the UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights was adopted. All member states are obliged to ensure that human rights are respected.
The UN keeps track of the human rights situation in the world and ensures that member states meet to preserve and strengthen human rights.
Sustainable development
The third core area is sustainable development. This work is summarised in the UN Sustainable Development Goals. There are 17 goals to, among other things, stop climate change, eradicate poverty and hunger, and ensure equality and good education. The goal is for the sustainability goals to be achieved by 2030.
The General Assembly
The General Assembly meets in sessions each year. A session of the UN General Assembly usually lasts from September to December. The General Assembly consists of representatives of all member states and its main task is to make recommendations to member states on issues related to international cooperation, peace and security, development and human rights. These recommendations are called resolutions. A UN resolution is of great importance. Although a resolution is only a recommendation to member states, it is to be seen as international public opinion. A two-thirds majority is required for a resolution in the General Assembly to be adopted. Each member state has one vote, and each vote counts equally.
Some UN organisations
The UN consists of a number of different organizations, funds, and programs that carry out the work of the UN. Some of these are:

UNICEF – The United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund. They work to help children all over the world. UNICEF’s governing document is called the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child. The Convention states that children are entitled to special protection.

UNESCO – The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. By collaborating in these fields, UNESCO contributes to peace and security. They want to inform, inspire and engage people to promote understanding and respect for each other and our planet.

WHO – The World Health Organization. They work to ensure that all people have the best possible state of health. WHO’s job is to monitor, research and provide people with reliable information about health and diseases. For example, WHO is a driving force behind the development of vaccines against dangerous diseases.

UNHCR – The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. They are responsible for promoting and protecting all human rights and freedoms set forth in the UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
These were some examples that show part of the work the UN does. There is great agreement in the world that the UN is the most important meeting place where all member states can talk together to agree on what rules should apply in international politics.
Work with words from the text
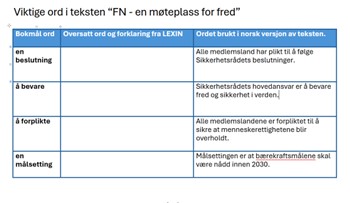
The assignment contains key words in the Norwegian text.
- Translate the words using LEXIN.
- In the right column, the word is used in a sentence found in the text. Translate or explain what the sentence means.
- Sources
- Fn-sambandet, https://fn.no/
- NDLA, FN – en verdensorganisasjon for fred – Samfunnskunnskap – NDLA







